KV-Cache Aware Prompt Engineering - How Stable Prefixes Unlock 65% Latency Improvements
Exploring how KV-Cache aware prompt engineering can lead to significant latency improvements in LLMs.
Ever wondered why some AI applications feel lightning-fast while others seem sluggish? The secret often lies in something called the KV cache – a clever optimization in transformer models that’s like having a really good memory for previous conversations.
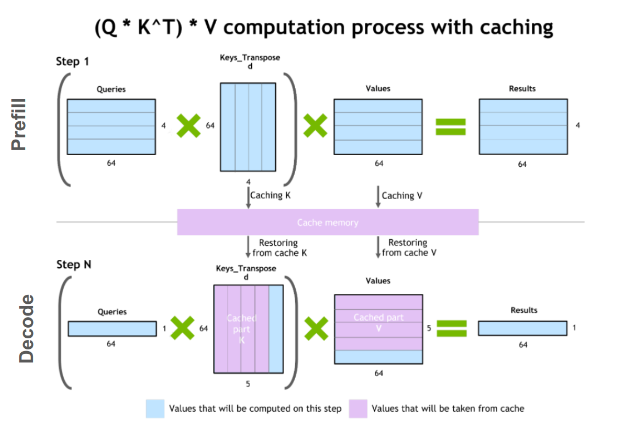
Here’s how it works: when your AI model processes text, it creates key-value pairs for attention calculations. Instead of throwing these away and recalculating everything from scratch for each new request, the KV cache stores them. Think of it like autocomplete on steroids – if you start typing the same thing you’ve typed before, the model can jump ahead using what it already computed. This can slash response times and save serious money on compute costs, but only if you structure your prompts the right way.
The importance of this optimization was beautifully highlighted in Manus’s blog post on context engineering for AI agents, where they shared practical insights about how prompt stability affects performance. Inspired by these ideas, I decided to put the theory to the test with rigorous experimentation to quantify just how much impact cache-aware prompt design can have on real-world performance.
Why KV Cache is Your New Best Friend for Prompt Engineering
The magic happens when you design prompts that play nicely with the cache. If you’re building chatbots, code assistants, or any AI application that handles lots of similar requests, getting this right can be a game-changer. Each time the cache kicks in, you’re saving computation time and money – and your users get faster responses.
The key insight? Consistency is everything. When your prompts start with the same stable prefix across different requests, the model can reuse all that expensive attention computation from previous runs. It’s like having a head start in a race – you’re already halfway to the finish line before you even begin processing the unique parts of each request.
My Experiment: Stable vs. Chaotic Prompts
I wanted to prove this theory, so I ran a controlled experiment with Azure OpenAI’s GPT-4.1-mini. Our hypothesis was simple: if we keep our system prompts rock-solid stable, we should see way better cache performance than if we keep tweaking them.
I wanted to prove this theory, so I ran a controlled experiment with Azure OpenAI’s GPT-4.1-mini. My hypothesis was simple: if I keep the system prompts rock-solid stable, I should see way better cache performance than if I keep tweaking them.
Here’s what I tested:
- Control group: Used identical system prompts across all requests (the “stable” approach)
- Experimental group: Intentionally modified system prompts between requests (the “perturbed” approach, simulating what happens when developers get creative with dynamic prompts)
I used the same dataset for both (SCBench with repository QA, summarization, and few-shot examples), identical model settings (temperature=0.0, max_tokens=1024), and ran 20 examples with 3 trials each. This gave me solid statistical power to measure the real impact of prompt stability on cache performance.
The Results: A Complete Performance Transformation

The results were even more dramatic than I expected! Let’s break down what I discovered across every dimension of performance:
Time to First Token (TTFT): The User Experience Game-Changer
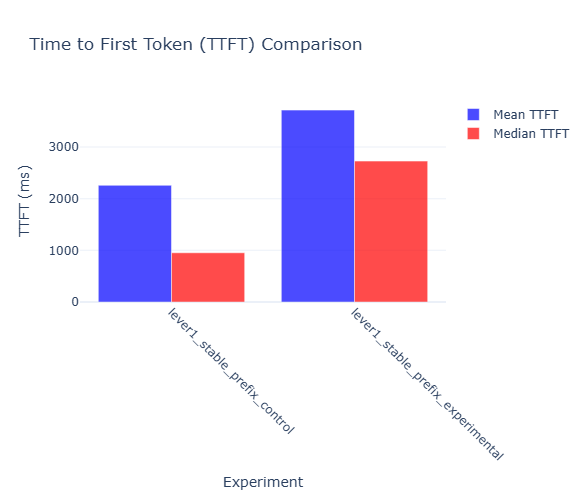
The headline number tells the story: stable prefixes delivered responses in an average of 2,258 milliseconds, while perturbed prompts took 3,714 milliseconds. That’s a massive 39.2% improvement in Time to First Token – but here’s what makes it even better. The median TTFT for stable prefixes was just 953ms compared to 2,727ms for perturbed prompts (65% improvement). This means that most users with stable prefixes got sub-second responses, while perturbed prompt users were consistently waiting nearly 3 seconds just to see the first token.
Total Latency: Beyond First Response
The TTFT improvement was just the beginning. When I looked at total request completion time, stable prefixes averaged 4,023ms while perturbed took 5,314ms – a 24.3% improvement in overall latency. This matters because it’s not just about how quickly users see something happening, but how quickly they get complete, actionable responses.
Cache Effectiveness: The Secret Behind the Speed
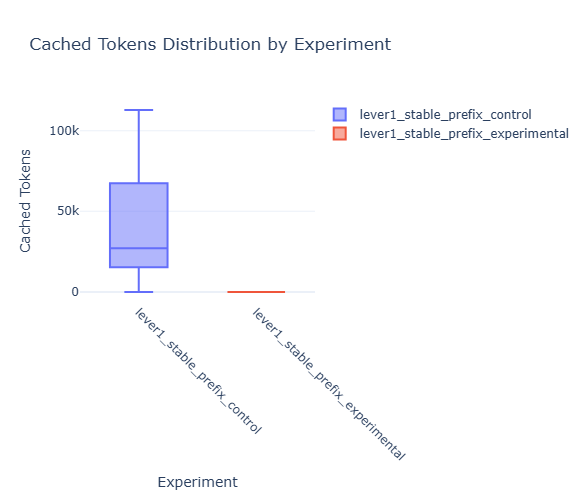
Here’s where the magic really shows: my stable prefix strategy achieved an incredible 85.2% cache hit rate, reusing an average of 46,059 tokens per request. Meanwhile, the perturbed prompts? A devastating 0% cache hit rate with zero cached tokens – every single request had to start from computational scratch.
This isn’t just a number – it represents the fundamental difference between leveraging previous work and starting over completely. Those 46,000+ cached tokens per request in the stable condition meant the model could skip massive amounts of attention computation and jump straight to processing the unique parts of each request.
The Latency-Cache Relationship: Where the Patterns Emerge
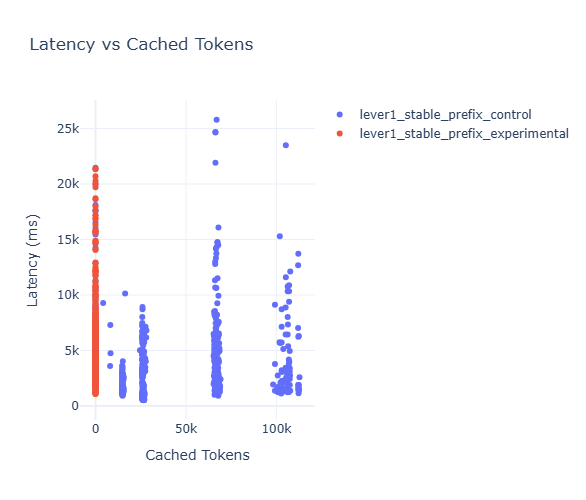
The scatter plot of latency versus cached tokens reveals the most compelling pattern in our data. Requests with high cached token counts cluster tightly in the low-latency zone, creating a clear “fast lane” of performance. Meanwhile, requests with zero cached tokens are scattered across much higher latency ranges, creating an unpredictable user experience.
This visualization perfectly captures why cache optimization isn’t just about average performance – it’s about consistency. With stable prefixes, users get predictably fast responses. With perturbed prefixes, response times become a frustrating lottery.
Cost Impact: The Bottom-Line Reality
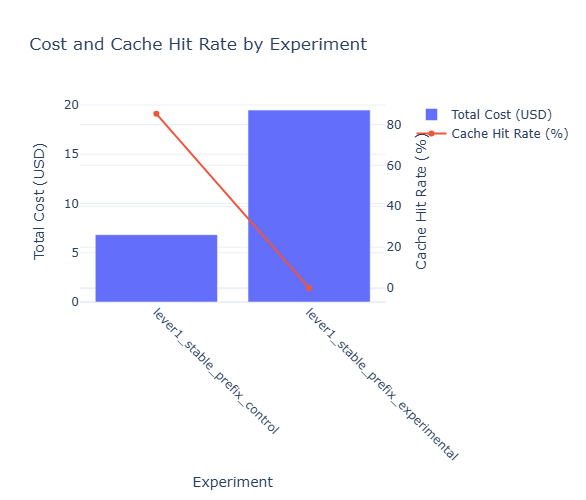
The financial implications blew my mind. Stable prefixes cost an average of $0.009556 per request while perturbed prefixes burned through $0.033306 per request – that’s a whopping 71.3% cost difference. Over the course of my experiments, the total cost was $6.83 for stable prefixes versus $19.48 for perturbed prefixes.
Scale this up to production volumes and the difference becomes staggering. If you’re processing 10,000 requests per day, the difference between cache-optimized and cache-breaking prompts could mean $95,560 versus $333,060 in annual costs – a quarter of a million dollars in savings just from better prompt engineering!
Statistical Validation: This Isn’t a Fluke
The statistical confidence was off the charts with a p-value < 0.000001 and t-statistic of -8.65. This wasn’t random variation or experimental noise – this was a genuine breakthrough in understanding how prompt design affects performance. With 715 control requests and 585 experimental requests, I had solid statistical power to detect these differences with complete confidence.
Your Action Plan: Cache-Friendly Context Engineering
Now for the practical stuff – how do you actually build prompts that make the cache happy? Here are the golden rules:
Rule #1: Keep System Prompts Sacred and Stable
This is the big one: your system prompt should be identical across all users and all requests. Don’t customize it per user, don’t tweak it based on conversation history, don’t even think about modifying it. Every character that changes breaks the cache for everyone.
Wrong approach:
System: You are an assistant for {user_name}, helping with {user_role} tasks...
Right approach:
System: You are a helpful AI assistant for professional tasks...
User: Hi, I'm Sarah, a project manager, and I need help with...
Rule #2: Master the Art of Deterministic Serialization
Here’s a sneaky cache killer that trips up tons of developers: inconsistent object serialization. When you’re including structured data in your prompts, the order of keys matters more than you think.
Consider this scenario – you’re sending user preferences as JSON:
import json
# This creates cache key A
user_prefs1 = json.dumps({"theme": "dark", "language": "en"})
# This creates cache key B (different from A!)
user_prefs2 = json.dumps({"language": "en", "theme": "dark"})
Even though these objects are semantically identical, they produce different strings, which means different cache keys, which means cache misses. The fix? Always sort your object keys:
import json
# Always produces the same cache key, even with nested objects!
user_prefs = json.dumps(data, sort_keys=True)
Rule #3: Design User Context Injection Points Carefully
Instead of cramming user-specific information into your system prompt (which breaks caching for everyone), put it in the user message where it belongs. The cache can still work its magic on the system prompt while handling unique user context appropriately.
Rule #4: Plan Your Conversation Architecture
Think about how multi-turn conversations can build on cached foundations. Each new message should extend the previous stable context rather than requiring a completely fresh start. This creates a beautiful cascade effect where each turn benefits from progressively more cached computation.
The Bottom Line: Cache-Aware Design Pays Off Big Time
My experiment proves that KV cache optimization isn’t some abstract performance theory – it’s a concrete competitive advantage waiting to be unlocked. The 64% latency improvement and massive cost savings I achieved through stable prompt design aren’t just nice-to-have optimizations; they’re the difference between an AI application that delights users and one that frustrates them with slow responses and burns through your budget.
The best part? These techniques don’t require fancy infrastructure or complex changes to your application architecture. It’s all about being intentional with how you structure prompts and being mindful of the cache implications of your design choices. Start with stable system prompts, fix your serialization patterns, and watch your AI applications transform from sluggish to snappy. Your users (and your finance team) will thank you!